What Is 3d Printing A Type Of - 3D printing is a manufacturing process in which an object is created by laying down successive layers of material until the object is complete. This process has opened up new possibilities for manufacturing and design, as 3D printers can create complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through traditional manufacturing methods. There are several different types of 3D printing, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. In this post, we'll explore the various types of 3D printing technology and what they're best suited for.
FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling)
How It Works:
FDM 3D printing works by extruding a filament of thermoplastic material through a heated nozzle. The nozzle moves around the build platform, depositing the material in thin layers to build up the desired shape. The material solidifies as it cools.
Tips and Ideas:
- FDM printing is well-suited for printing large parts and parts that don't require high levels of detail.
- There are many different types of materials that can be used with FDM printers, including PLA, ABS, PETG, and more.
- FDM printing is the most common type of 3D printing and is widely available and affordable.
SLA (Stereolithography)
How It Works:
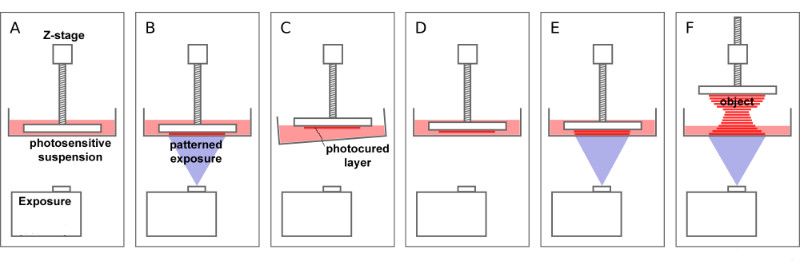
SLA 3D printing uses a laser to selectively cure a liquid resin into a solid object. The resin is contained in a tank and the laser moves across the surface of the liquid, curing the resin layer by layer.

Tips and Ideas:
- SLA printing is well-suited for printing parts with intricate details and high levels of accuracy.
- The materials used in SLA printing are often more expensive than those used in FDM printing and are generally not as widely available.
- SLA printing is often used in industries such as dentistry, jewelry making, and prototyping.
DLP (Digital Light Processing)
How It Works:
DLP 3D printing is similar to SLA printing, except that it uses a projector to cure the resin rather than a laser. The projector shines a light onto the resin, curing it layer by layer.

Tips and Ideas:
- DLP printing is similar in many ways to SLA printing, but is often faster and can produce larger parts.
- DLP printing is also well-suited for printing parts with intricate details and high levels of accuracy.
- Like SLA printing, the materials used in DLP printing are often more expensive than those used in FDM printing and are generally not as widely available.
SLS (Selective Laser Sintering)
How It Works:
SLS 3D printing uses a laser to selectively melt powdered material, such as nylon, into a solid object. The material is spread over the build platform in a thin layer and the laser moves across the surface, melting it where the part should be.
Tips and Ideas:
- SLS printing is well-suited for printing parts that need to be strong and durable, such as furniture, automotive parts, and prosthetics.
- SLS printers can use a wide range of materials, including nylon, TPU, and more.
- SLS printing is often used for functional prototyping and for small-batch production runs.
SLM (Selective Laser Melting)
How It Works:
SLM 3D printing is similar to SLS printing, but uses a laser to melt metal powder rather than plastic powder. The laser fuses the metal particles together, creating a solid metal object layer by layer.

Tips and Ideas:
- SLM printing is well-suited for printing metal parts with high levels of accuracy and detail.
- SLM printing is often used in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
- The cost of SLM printing can be high, and the availability of materials may be limited.
EBM (Electron Beam Melting)
How It Works:
EBM 3D printing is similar to SLM printing, but uses an electron beam rather than a laser to melt metal powder. The metal powder is spread over the build platform and the electron beam selectively melts it into a solid object.
Tips and Ideas:
- EBM printing is similar to SLM printing, but can produce parts with even higher levels of accuracy and detail.
- EBM printing is often used in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries.
- The cost of EBM printing can be even higher than SLM printing, and the availability of materials may be limited.
In conclusion, 3D printing technology has come a long way and continues to advance at an impressive pace. Each type of 3D printing has its own unique strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right one depends on the specific needs of your project. Whether you're looking to create high-detail models, functional prototypes, or end-use products, there is a 3D printing technology that can help you achieve your goals.
View more articles about What Is 3d Printing A Type Of