3D Printing vs Injection Moulding - which manufacturing process is right for your product? It's a question that many entrepreneurs and product designers ask themselves. While both processes are used to create plastics, there are differences in terms of cost, quality, and timing. In this post, we will explore the pros and cons of 3D printing vs injection moulding to help you make an informed decision about which process is right for you.
What is Injection Moulding?
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process used to create parts by injecting molten material into a mould. The material, typically plastic, is injected under high pressure into a mould cavity. The mould is then cooled, and the part is ejected. Injection moulding is ideal for creating large quantities of identical parts with a high degree of accuracy and consistency.
Pros of Injection Moulding:
- Economies of Scale: Injection moulding is ideal for high-volume productions, making it economically feasible for large quantities.
- Consistency: Injection moulding ensures consistent quality throughout the production process, ensuring the product's reliability and functionality.
- Speed: Injection moulding is a fast process; it can produce thousands of parts per hour, making it ideal for rush orders and tight deadlines.
Cons of Injection Moulding:
- High Initial Cost: Injection moulding equipment, tooling, and design require a significant initial investment.
- Long Lead Time: The development and optimisation of an injection mould can take several weeks or even months, depending on the complexity of the design.
- Inflexibility: The process and the mould are geared towards high volume production runs, making it less suitable for small runs and prototyping.
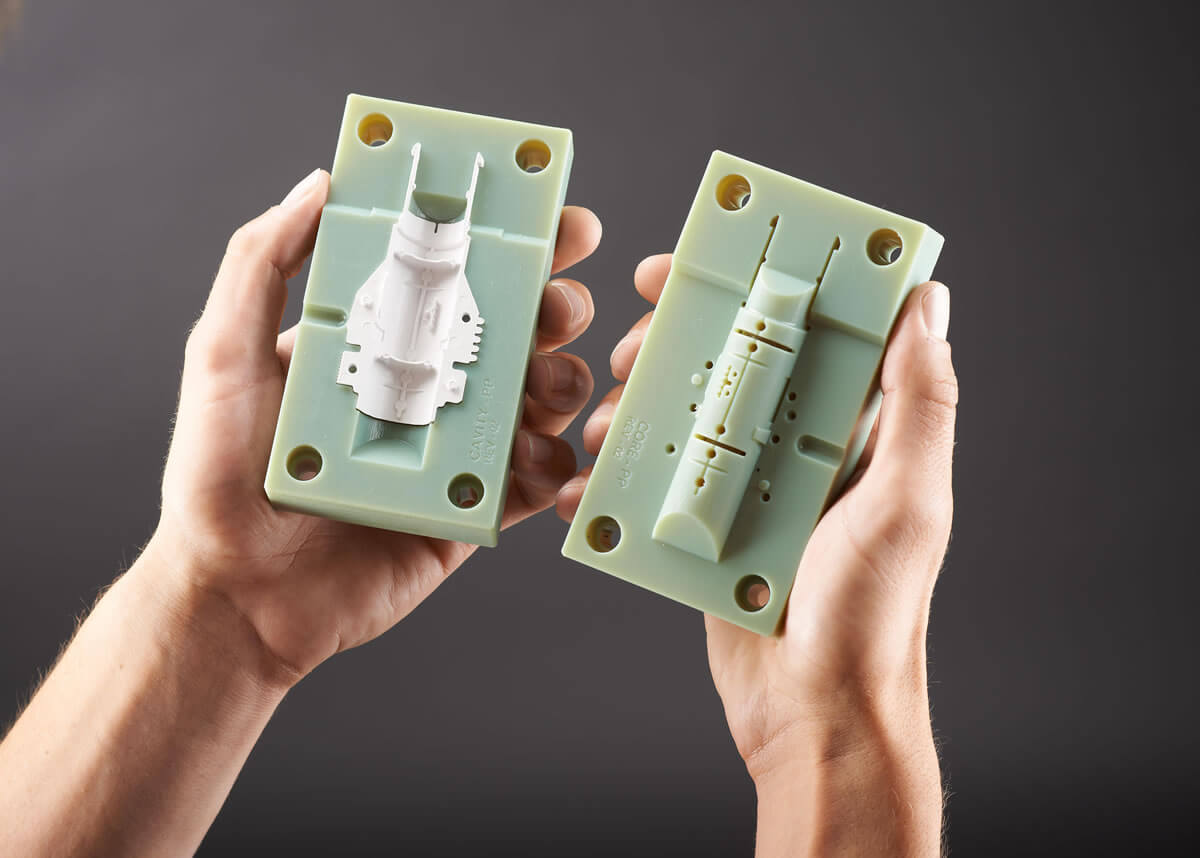
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves building up layers of material to create a three-dimensional object. The material used is typically a thermoplastic, and the process is controlled by a computer-aided design (CAD) program, which guides the printer's nozzle to build the part layer by layer.
Pros of 3D Printing:
- Low Initial Cost: 3D printing requires less initial investment, making it ideal for small runs and prototyping.
- Flexibility: 3D printing allows for quick and easy changes to the design, making it easier to iterate on new ideas.
- Speed: 3D printing is fast, making it ideal for tight deadlines and rush orders.
Cons of 3D Printing:
- Low-Quality Output: 3D printers produce lower quality parts than injection moulding, making them less suitable for mass production runs and end-use products.
- Limited Material Options: Currently, 3D printing can only use a limited range of materials, making them less versatile than injection moulding machines.
- Limited Production Runs: 3D printing is less economical for high volume runs, making it less suitable for mass production runs.

How to Choose Between 3D Printing and Injection Moulding?
So, how do you choose between 3D printing and injection moulding? The answer depends on your product, project timeline, and budget. Here are some tips to help you decide:Project Timeline:
If you need your parts quickly, 3D printing might be the best choice for your project. But if you are planning a mass production run, injection moulding might be the better option since it can produce more parts in less time.Quantity of Parts:
How many parts do you need to produce? Injection moulding is great for mass production runs, but it might not make sense for smaller runs. 3D printing is better suited for smaller runs since it requires less equipment and set-up time.Product Quality:
Is your product going to be used in demanding applications? If yes, injection moulding might be the better choice since it produces higher quality parts that can withstand wear and tear. 3D printing is more suitable for prototyping since it doesn't produce parts that can handle the same level of stress as injected moulded parts.Design Complexity:
How complex is your design? Injection moulding is better suited for designs that require intricate details or fine lines. 3D printing is better for designs with fewer details that can be built up layer by layer.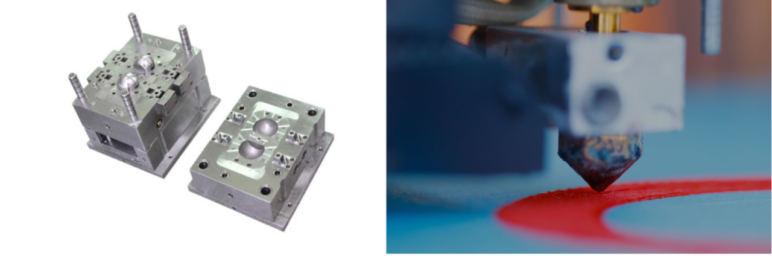
Conclusion:
While 3D printing and injection moulding are both excellent tools, they are best suited for different types of projects. Understanding the advantages and limitations of each process is critical in deciding which one to use for your project. Our team of manufacturing experts can help you choose the right manufacturing process for your product. Contact us today to learn more about how our services can help bring your vision to life.
Find more articles about 3d Printing Vs Injection Moulding